Essential Knowledge on Backup Power
- Sonja Joubert

- Mar 25, 2025
- 2 min read
Load-shedding is a challenge, but with the right knowledge, you can keep your home or business running smoothly. That’s why we’re launching a Power Backup Tips Series — simple, practical advice to help you make the most of your backup power solutions!
Power Basics

In this first edition, let’s break down some power basics:
🔌 Voltage (V) = The Push Think of voltage like water pressure in a hose. The higher the voltage, the stronger the push of electricity.
⚡ Amps (A) = The Flow Amps are like the amount of water flowing through the hose. More amps mean more electricity moving at once.
💡 Watts (W) = The Power Watts tell you how much total power is being used. It’s like how much water comes out of the hose every second. (Watts = Volts x Amps)
What is Watt-Hours?

Watt-hours (Wh) = Energy Stored & Used Over Time
If watts tell you how much power is used at a moment, watt-hours tell you how long something can run.
Imagine you have a 100W lightbulb — if it runs for 1 hour, it uses 100Wh of energy. If it runs for 5 hours, that’s 500Wh. The more watt-hours your battery has, the longer your devices can stay powered!
Example: A 500Wh battery can power a 100W light for 5 hours, or a 50W fan for 10 hours.
The Simple Guide to Power

Water Pressure = Voltage
Water Flow = Amps
Pipe Size = Ohms (Resistance)
Energy Produced = Watts
Backup Power Display
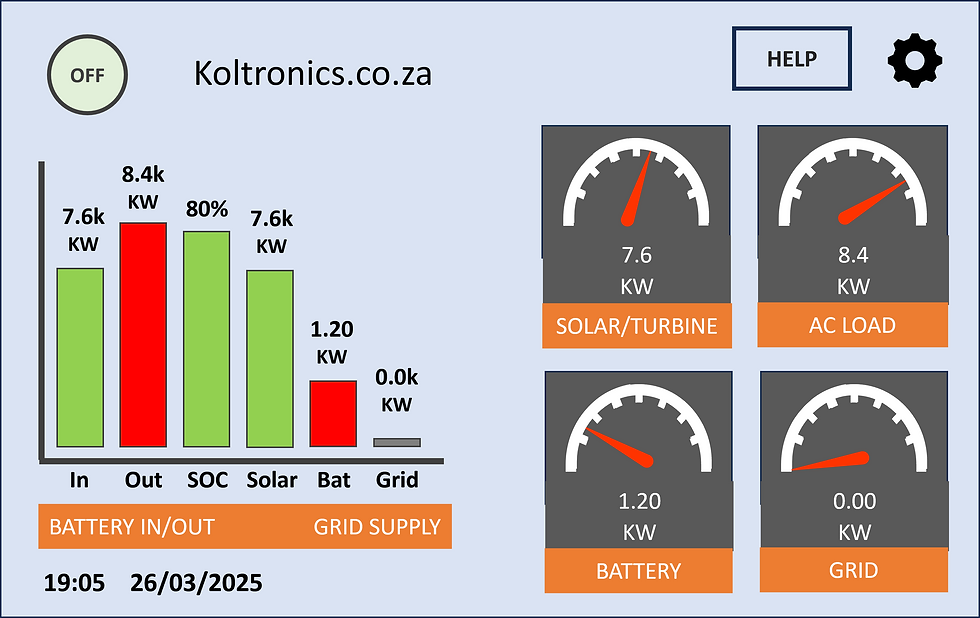
What you’ll typically might see on your Backup System display screen:
Battery Voltage: Helps monitor battery charge levels.
Current Load (Watts): Shows how much power your devices are using.
Battery % Remaining: Helps estimate how much time you have left before recharging is needed.
Power Input: Displays how much power is coming from Eskom or solar panels if applicable.
By understanding these readings, you can better manage your power usage and extend your backup system’s runtime!




Comments